Common methods of text analysis
Text analysis was the first digital humanities project. [1]
Involves applying computational methods to large collections of texts (corpora) to extract insights, known as distant reading (vs. traditional close reading).
Common methods include:
- Concordances : Analyze word frequency and locations within texts.
- Topic Modeling: Identify recurring themes using computational linguistics.
- Stylometry [2]: Study writing style statistically to attribute authorship or identify genre features.
- Uncovering patterns : Unveil biases, assumptions, and hidden meanings, offering fresh perspectives and deeper insights.
- Sentiment analysis : Evaluate and interpret emotions, opinions, and attitudes expressed in text, helping to understand public sentiment, customer feedback, and social trends.
Sources:
[1] Chris Alen Sula, Heather V Hill, The early history of digital humanities: An analysis of Computers and the Humanities (1966–2004) and Literary and Linguistic Computing (1986–2004), Digital Scholarship in the Humanities, Volume 34, Issue Supplement_1, December 2019, Pages i190–i206, https://doi.org/10.1093/llc/fqz072
[2] Cammarota, V., Bozza, S., Roten, C.-A., & Taroni, F. (2024). Stylometry and forensic science: A literature review. Forensic Science International: Synergy, 9, 100481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsisyn.2024.100481
Timeline of text analysis evolution from early computer-assisted analysis to modern AI-driven approaches (1960-2024)
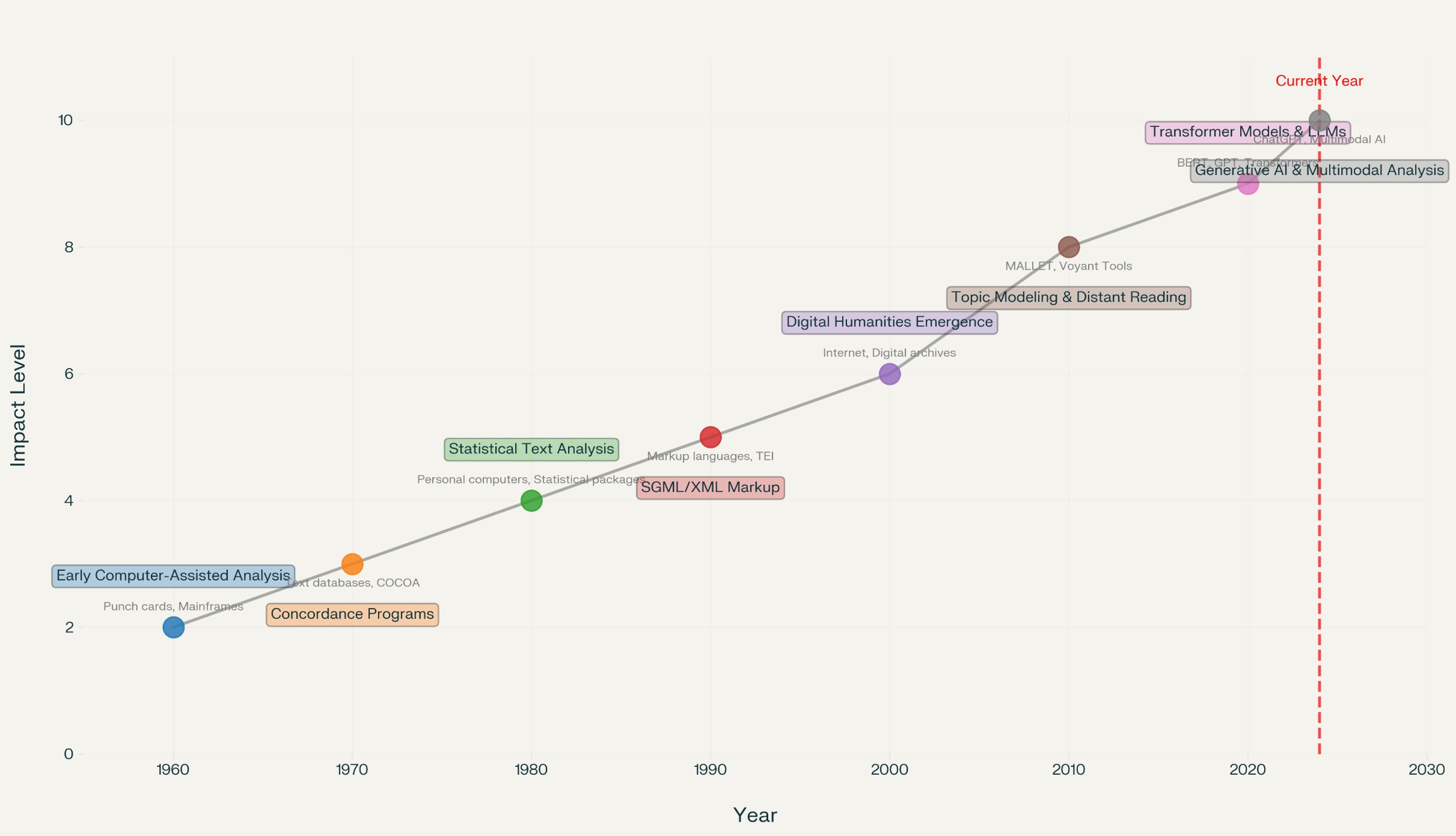
This graph was generated by Perplexity Pro Lab on 15-07-2025
